Strength / Gear Tooth Contact Stress¶
Authors: Tugan Eritenel
Description: Calculation of gear tooth contact stress in spur gears.
Table of Contents¶
Introduction¶
This chapter is on contact stress of parallel axis gears.
Contact Stress Theory¶
Gear tooth contact along the tooth surface can be considered as a line. The width of the contact is much shorter than the length along the line of contact. The radius of curvatures of the contacting surfaces vary as the gears rotate. Maximum subsurface shear stress is just below the point of contact. The mechanism of stress is quite complicated due to sliding and friction between the surfaces.
Stresses on gear tooth.
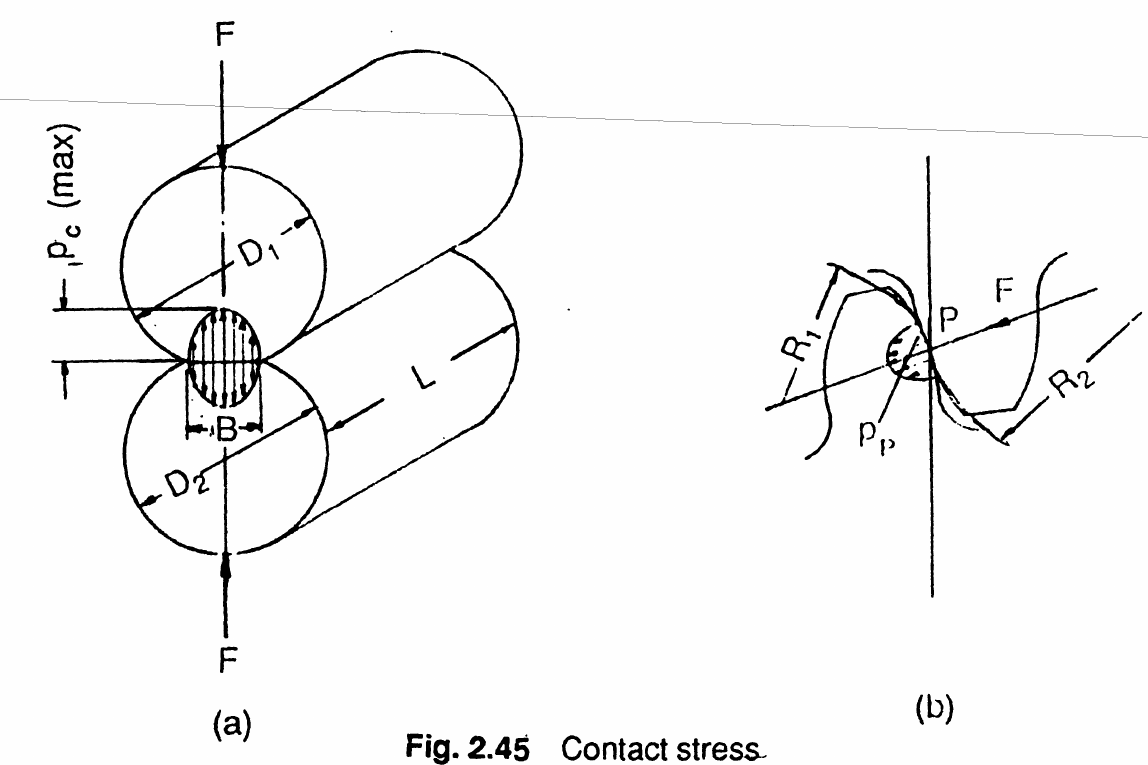
Image credit: G. M. Maitra, Handbook of Gear DesignPitting is a type of gear failure as a result of subsurface contact stress cycles. The contact stress is denoted with the symbol $p$ referring to Hertzian pressure developed. The maximum pressure on two cylinders in contact is given by,
$$ p_{c(max)} = \frac{4 F}{\pi B L}$$where the width of the contact is calculated as,
$$B = \sqrt{\frac{8 F}{\pi L} \frac{\left(1-\nu_1^2\right)/E_1 + \left(1-\nu_2^2\right)/E_2}{\left(1/D_1\right) + \left(1/D_2\right)}}$$Gear Contact Stress Calculation¶
When the elastic modulus of the two cylinders are the same $E_1 = E_2$, and poisson ratio are $\nu_1 = \nu_2 = 0.3$, the contact pressure for gears becomes,
$$ p_p = \sqrt{0.35\frac{F_t E}{b d_{p,1}} \frac{i+1}{i} \frac{1}{\cos^2\alpha \tan\alpha_w}} $$A few parameters are factored so that from the equation above as follows,
$$ p_p = y_m y_p \sqrt{\frac{F_t}{b_1 d_{p,1}} \frac{i+1}{i}}$$where material factor $y_m$ and tooth shape factor, $y_p$, are given by,
$$y_m = \sqrt{0.35 E}$$ $$y_p = \sqrt{\frac{1}{\cos^2\alpha \tan\alpha_w}} $$For a first design iteration, assuming no profile shift, and $\alpha = 20^{\circ}$, $y_p = 1.76$, and $E=206,000$ MPa, so $y_m = 269$.
Maximum allowable surface fatigue stress $p_{sc}$ needs to be determined from the gear material. For example, induction hardened 40 Cr 4 allowable surface fatigue stress is 1620 MPa. Generally a factor of safety of 1.5 is applied, giving the contact pressure limit as $p_{cp}< \frac{p_{sc}}{1.5}$.
Contact pressure is written in terms of applied torque as,
$$ p_{cp} = y_m y_p\sqrt{ \frac{2000 T_1}{\left(b/d_{p,1}\right) d_{p,1}^3} \frac{i+1}{i}}$$Minimum module to satisfy contact pressure safety is found according to,
$$ m_n > \frac{1}{z_1} \sqrt[3]{ \frac{2000 T_1 y_m^2 y_p^2}{\left(b/d_{p,1}\right) p_{cp}^2} \frac{i+1}{i}}$$Example | Tooth Contact Stress
GIVEN
- A gear pair has 45 teeth on the pinion and 137 teeth on the wheel.- Torque on the pinion is 600 Nm.
FIND
1) Minimum module so that the pinion is safe for contact fatigue.2) Contact pressure on pinion tooth flank.
SOLUTION
For the first iteration of design $y_p = 1.76$ and $y_m=269$. The ratio of facewidth to pitch diameter is taken as $b_1 / d_{p,1} = 0.5$ to provide a starting point for the design. The formula below is used for finding the minimum module. Substituting the given values, the minimum module for contact is:Conclusion¶
This notebook documents the procedure to find spur gear contact stress. Inputs are a few parameters from gear macro geometry: number of teeth, pressure angle, and applied torque. Minimum module is found so that the gears are safe considering contact stress. For a chosen module and the gear parameters above, contact stress is calculated.
Learn More
Continue reading the Drivetrain Hub | Notebook Series to learn more about the design and analysis of spur gears and other gear types.
Model Gear Contact
Accurately model the contact of a gear mesh with the Drivetrain Hub | Gears App, a modern drivetrain modeling environment 100% online at drivetrainhub.com.
Improve Notebook
Our gear geometry notebooks are publicly hosted in a GitHub repository, available for anyone to view and propose edits.
References¶
- G. M. Maitra, (1994), "Handbook of Gear Design", Tata McGraw-Hill
